The water footprint is an indicator of freshwater use that looks not only at direct water use of a consumer or producer, but also at the indirect water use. The water footprint of a product is the volume of freshwater used to produce the product, measured over the full supply chain, either externally (by importing products) or internal (when these are produced in the country). This concept can be expanded to provide the water footprint of nations or even continents.
The Water footprint is an analytical tool that can address political issues of water security and sustainable use of water. The water footprint shows the quantity and location of water usage in relation to population consumption.
The water footprint of a product is the volume of freshwater used to produce the good or service, measured in the place where de good was produced. The Water Footprint of a product in the amount of water used in the different stages of the production chain, also known as virtual water content.
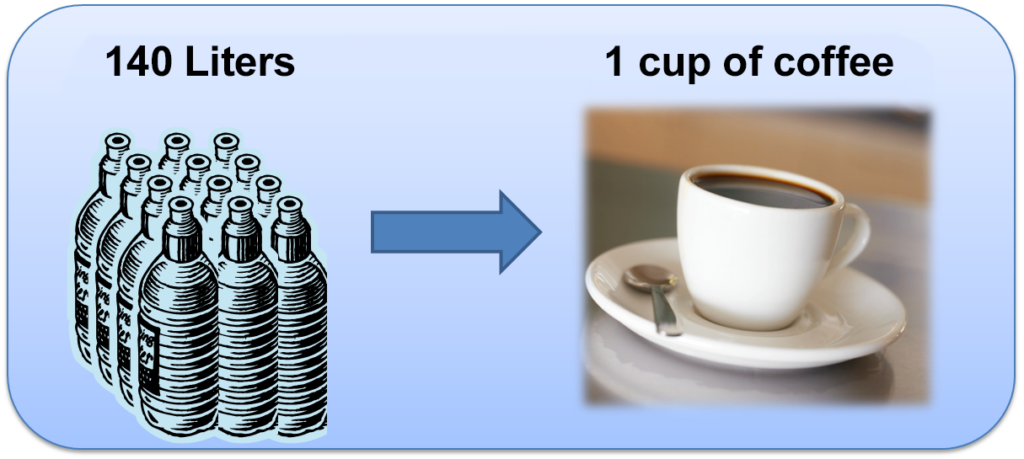
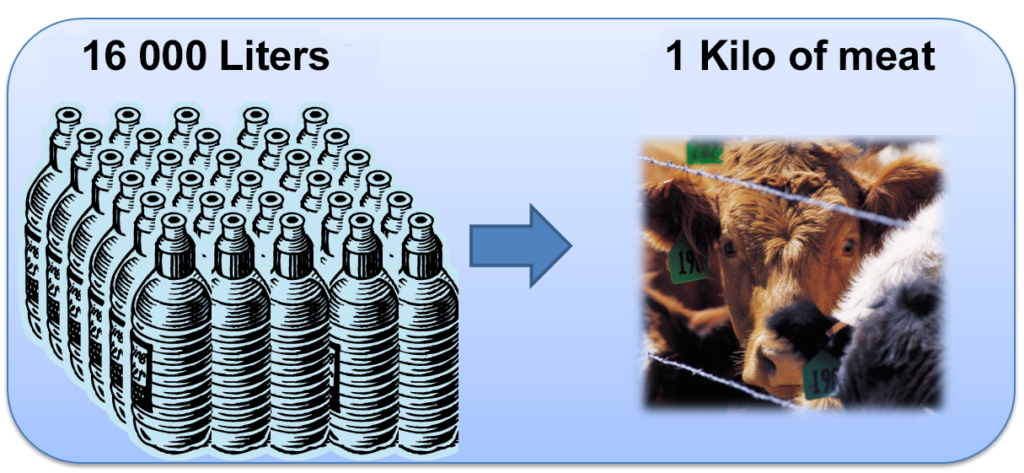
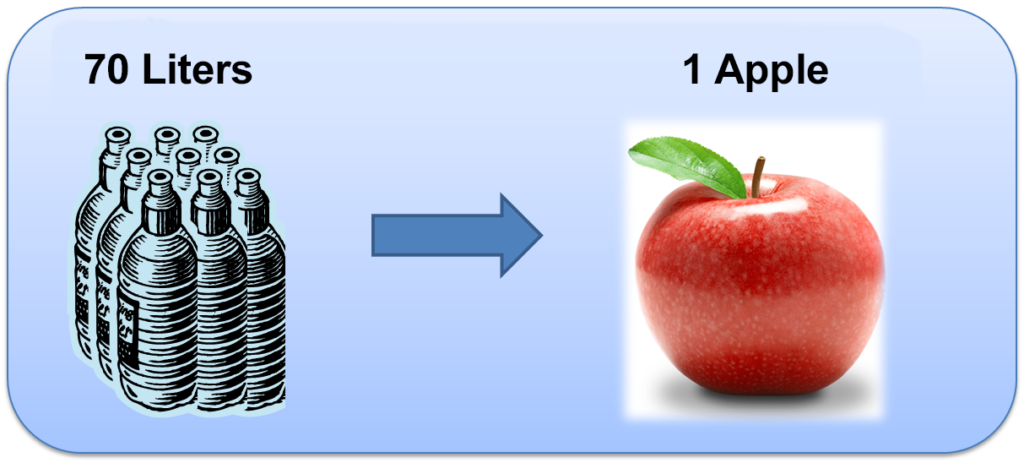
Pictures from the Water Foot Print Organization
The water footprint of a community is defined as the volume of water used for the production of goods and services that are consumed by members of a community.
The water footprint of a nation is an indicator of the effects of domestic consumption of water, considering the internal and external resources. The ratio of internal / external water consumption is important because outsourcing the water footprint means more dependence on foreign water resources. Outsourcing also results in environmental impacts that the consumption / use of water involves.
Water use is measured in terms of volume of water consumed (evaporated) and / or polluted per unit of time. The water footprint is a geographically explicit indicator because it shows the volumes of water used and polluted, and also the locations.
Components of the water footprint: The total water footprint of an individual or community breaks down into three:
The volume of fresh water evaporated from the global resources of surface and groundwater to produce goods and services consumed by the individual or the community.
The amount of water evaporated from the global green water resources (rainwater stored in the soil).
The volume of contaminated water, which can be calculated as the volume of water that is required to dilute pollutants to such an extent that the quality of the ambient water remains above agreed water quality standards.